The Details of Industrial Design
- Josephine
- May 11, 2025
- 3 min read
The details in industrial design cover many aspects. Here are some common points:
Product appearance details lines and contours:
The smoothness of the lines, the naturalness of the arc, and the clarity of the contours will affect the overall beauty and quality of the product.
For example, the border lines of Apple mobile phones are simple and smooth, with natural transitions, giving people a sense of refinement. Color matching: The choice of color should not only consider aesthetics, but also match the function, positioning, and user psychology of the product. For example, medical equipment usually uses cold colors such as white or light blue, giving people a sense of professionalism, safety, and cleanliness. Surface treatment: Including frosting, polishing, brushing, spraying and other processes, different surface treatment methods will bring different textures and touches to the product.

For example, the body paint of a car, high-quality spray paint is not only bright in color, but also has good wear resistance and corrosion resistance. Corner treatment: The corners of the product are where users often touch. The design of rounded corners, chamfers or right angles and the smoothness of the corners will affect the feel and safety of the product.
Like some children's products, the corners are usually designed to be rounded to prevent children from getting hurt. Product structure details Component connection: The connection between components should be firm and reliable, and the convenience of assembly and disassembly should be considered.
For example, snap-on connection can facilitate product assembly and maintenance, while welding can provide a more stable connection.
Internal layout: Reasonable internal layout can effectively utilize space and improve product performance and heat dissipation.
For example, the various hardware components inside the computer host are compactly laid out, while leaving enough heat dissipation channels to ensure the stable operation of the computer.
Material selection: Select appropriate materials according to the function and use environment of the product. The strength, toughness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance and other properties of the material must meet the requirements of the product.
For example, high-temperature alloy materials are required to manufacture aircraft engine blades to withstand high temperature and high pressure working environments.
Product function details Operational convenience: The design of the product's operating buttons, knobs, handles, etc. should conform to ergonomic principles and be convenient for users to operate.
For example, the steering wheel design of a car should be easy for the driver to hold and operate, and the position and size of various control buttons should conform to human operating habits.
Functional rationality: The functional design of the product should meet the actual needs and usage scenarios of users, and the logical relationship between functions should be clear.
For example, the camera function of a mobile phone should have a simple and clear operation process from opening the camera application to taking a photo, and various shooting modes and function buttons should be easy to find and use.
Feedback mechanism: When users operate the product, timely feedback should be given to let users know the results of the operation.
For example, there should be clear tactile feedback or sound feedback when a button is pressed, and there should be corresponding prompt information on the screen of the electronic device.
User experience details Ease of use: The product should be easy to understand and use, and users do not need to spend too much time and energy to learn.
For example, some smart home appliances allow users to operate easily through simple interface design and voice control functions.
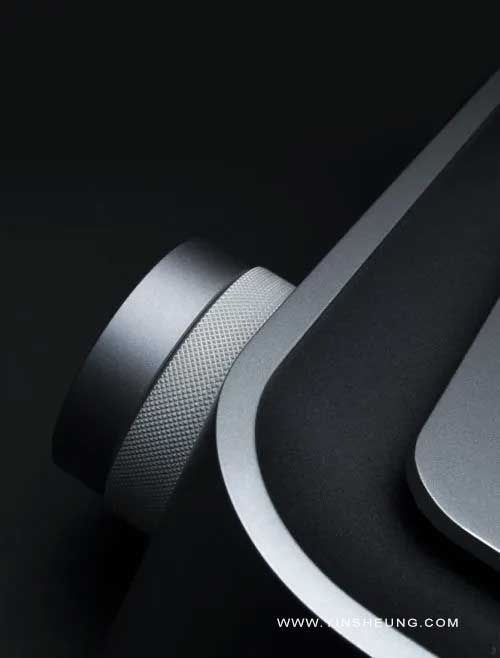

Comfort: Consider the comfort of users in the process of using the product, including physical comfort and psychological comfort.
For example, the design of office chairs should conform to the human body curve, provide good support and comfort, and reduce the fatigue of users sitting for a long time.
Emotional design: convey emotions and personality through design elements, so that users can resonate with the product emotionally.
For example, some products with unique shapes or cultural connotations can meet the personalized needs and emotional appeals of users.
The processing of details in industrial design is crucial, as it directly affects the quality, user experience and market competitiveness of the product. Designers need to consider details from multiple angles and integrate details into every aspect of product design to create excellent products.



Comments