Some Knowledge About 6 series aluminum alloy -6061
- Josephine
- Jun 21, 2025
- 2 min read
The gas absorption of metal is determined by the ability of metal to combine with gas. The bonding force between 6061 aluminum metal and gas is different, and the solubility of gas in metal is also different.
Metals and alloys with high vapor pressure can reduce gas content due to evaporation and adsorption. Alloy elements with greater bonding force with gas will increase the solubility of alloy. Elements with less bonding force with gas, on the contrary, increase the solidification temperature range of alloy, especially elements that reduce the solidus temperature, which is easy to cause pores and looseness in ingots.
Copper, silicon, manganese, and zinc all reduce the solubility of gas in aluminum alloys, while titanium, zirconium, and magnesium are the opposite.
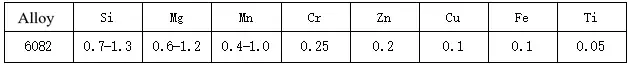
The influence of alloy composition on the mechanical properties of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy
The main alloying elements of 6061 aluminum alloy are magnesium and silicon, which form Mg2Si phase. If a certain amount of manganese and chromium are contained, the bad effects of iron can be neutralized. Sometimes a small amount of copper or zinc is added to improve the strength of the alloy without significantly reducing its corrosion resistance. There is also a small amount of copper in the conductive material to offset the adverse effects of titanium and iron on conductivity. Zirconium or titanium can refine the grains and control the recrystallization structure. Lead and bismuth can be added to improve the machinability.
The main strengthening material Mg2Si is dissolved in aluminum to give the alloy an artificial aging hardening function. Therefore, in order to have better mechanical properties, qualified chemical composition is a prerequisite, especially the formation of the main strengthening phase Mg2Si. It is necessary to ensure that the chemical composition meets the national standard requirements so that good mechanical properties can be obtained after later processing.



Comments