Effects of chemical elements in aluminum alloys on product performance
- Josephine
- May 2, 2025
- 4 min read
The following article comes from aluminum high-end manufacturing.
Aluminum high-end manufacturing.
The latest technology and development trends in the research, processing and application of light metal materials! Provide an open platform for extensive communication and cooperation for the majority of material science and technology workers!
Global aluminum partner
, like 16
Different alloying elements will have the following effects on the performance of aluminum alloy materials:
Strength and hardness: Adding alloying elements can change the strength and hardness of aluminum alloys. For example, copper and magnesium can increase the tensile strength and yield point of aluminum alloys, making them stronger and more durable.
Corrosion resistance: Certain alloying elements can enhance the corrosion resistance of aluminum alloys, making them more stable in various environments. For example, elements such as nickel, chromium and silicon can increase corrosion resistance.
Thermal properties: Alloying elements have a significant effect on the thermal conductivity and thermal expansion coefficient of aluminum alloys. For example, silicon can increase thermal conductivity, while magnesium increases the thermal expansion coefficient.
Plasticity and toughness: The addition of alloying elements can change the plasticity and toughness of aluminum alloys, making them more suitable for various processing and forming processes. For example, an appropriate amount of manganese can improve ductility and toughness.
Conductivity: Alloying elements have a significant effect on the conductivity of aluminum alloys. For example, copper can increase conductivity, while nickel will reduce conductivity.
Fatigue resistance: Certain alloying elements can improve the fatigue resistance of aluminum alloys, making them less likely to break under repeated stress. For example, magnesium and manganese can improve fatigue resistance.
Machinability: The addition of alloying elements can change the machinability of aluminum alloys. For example, an appropriate amount of zinc can improve cutting performance, while silicon can improve casting performance.
By reasonably selecting and matching alloying elements, aluminum alloy materials with the required properties can be customized to meet various different application requirements.
The chemical composition of aluminum alloys mainly includes aluminum, silicon, copper, magnesium, zinc, manganese and other elements. Among them, aluminum is the main component, and the content is generally above 95%. Other elements are added as alloying elements to improve the properties of aluminum alloys.
The most widely used elements in aluminum alloys are copper, magnesium, zinc and silicon. These elements play an important role in aluminum alloys and can significantly improve the properties of aluminum alloys.
Copper: Copper is one of the common additive elements in aluminum alloys, which can improve the strength and hardness of aluminum alloys, and also improve their corrosion resistance. Copper can also improve the heat treatment properties of aluminum alloys, making them have better heat treatment plasticity.
Magnesium: Magnesium is also one of the important alloying elements in aluminum alloys. It can improve the tensile strength and yield point of aluminum alloys, while improving their fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance.
Zinc: Zinc is mainly used to improve the corrosion resistance of aluminum alloys. It can form a dense oxide layer with aluminum to prevent further oxidation reactions, thereby improving the corrosion resistance of aluminum alloys.
Silicon: Silicon is one of the elements with a higher content in aluminum alloys, which can improve the strength and hardness of aluminum alloys. At the same time, silicon can also improve the casting properties and wear resistance of aluminum alloys.
Copper, magnesium, zinc and silicon are the most widely used elements in aluminum alloys. The addition of these elements can significantly improve the properties of aluminum alloys and meet various different application requirements.
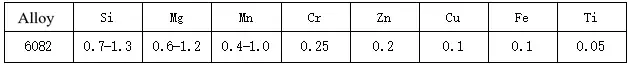
Silicon is an element with a high content in aluminum alloys, and its content is usually between 4.5% and 11%. Silicon can improve the tensile strength and yield point of aluminum alloys, and at the same time enhance corrosion resistance.
Copper is also one of the common alloying elements in aluminum alloys, and its content is usually between 1.2% and 2.0%. Copper can increase the strength and hardness of aluminum alloys, and improve their wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
Magnesium is also one of the important alloying elements in aluminum alloys, and its content is usually between 0.4% and 1.2%. Magnesium can improve the tensile strength and yield point of aluminum alloys, and at the same time improve their fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance.
Zinc and manganese are also common alloying elements in aluminum alloys, which can improve the plasticity and processing properties of aluminum alloys, and improve their strength and corrosion resistance.
The most widely used elements in aluminum alloys are copper, magnesium, zinc and silicon. These elements play an important role in aluminum alloys and can significantly improve the properties of aluminum alloys. Copper: Copper is one of the common additive elements in aluminum alloys, which can improve the strength and hardness of aluminum alloys, and at the same time improve their corrosion resistance. Copper can also improve the heat treatment properties of aluminum alloys, making them have better heat treatment plasticity. Magnesium: Magnesium is also one of the important alloying elements in aluminum alloys. It can improve the tensile strength and yield point of aluminum alloys, while improving their fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance. Zinc: Zinc is mainly used to improve the corrosion resistance of aluminum alloys. It can form a dense oxide layer with aluminum to prevent further oxidation reactions, thereby improving the corrosion resistance of aluminum alloys. Silicon: Silicon is one of the elements with a higher content in aluminum alloys, which can improve the strength and hardness of aluminum alloys. At the same time, silicon can also improve the casting properties and wear resistance of aluminum alloys. In short, copper, magnesium, zinc and silicon are the most widely used elements in aluminum alloys. The addition of these elements can significantly improve the performance of aluminum alloys and meet various different application requirements.
In addition, aluminum alloys may also contain a small amount of iron, titanium, chromium and other elements, which also have a certain effect on the performance of aluminum alloys. The chemical composition of aluminum alloys will vary according to different uses and performance requirements. Through a reasonable ratio of alloying elements, aluminum alloy materials with excellent performance can be produced.



Comments